Most likely, many of us have heard such a thing as MRI and MSCT at least a couple of times in our lives. Let's figure out what it is.
In medicine, magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) and multispiral computed tomography (MSCT) occupy leading positions among imaging methods. These technologies allow doctors to "look" inside the human body without surgery, providing valuable information for the diagnosis and treatment of various diseases.
MRI and MSCT, although they perform similar functions, are based on different principles and have different characteristics. That is why it is important to understand their differences in order to choose the most appropriate diagnostic method for a particular case.
In this article, we will take a detailed look at what MRI and MSCT are, identify their key differences and try to answer the question of which of these methods is best suited in a given situation. This will help you better understand what questions to ask your doctor when choosing a diagnostic method.
What is MRI (Magnetic Resonance Imaging)?
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is a medical imaging technique that uses a powerful magnetic field and radio waves to create detailed images of the internal structures of the body. Unlike X-rays and computed tomography (CT) scans, MRI does not use ionizing radiation, which makes it a safer choice for patients.
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) works on the basis of a magnetic field and radio waves. During the MRI procedure, a strong magnetic field aligns the hydrogen atoms in the human body in one direction. Then the radio waves disrupt this ordered state, and after they are turned off, the atoms return to their original position. During the return process, the atoms emit signals that MRI detectors capture and convert into clear images of the internal structures of the body. Thus, MRI allows doctors to get a detailed picture of what is happening inside the body without resorting to surgery.
MRI is most effective for studying the soft tissues of the body. It is widely used to diagnose diseases of the brain and spinal cord, including tumors, strokes and degenerative diseases. MRI is also used to assess the condition of joints, cartilage, ligaments, as well as in cardiology and oncology.
What are the advantages of MRI
- High accuracy and detail: MRI provides clear images of soft tissues, which makes it indispensable for the diagnosis of many diseases.
- Safety: The absence of ionizing radiation makes MRI the preferred method, especially for children and pregnant women.
- Visualization: MRI can provide images in different planes and even show the functional activity of the brain.
Now let's learn more about MSCT to better understand what are the key differences between these two diagnostic methods.
What is MSCT (Multispiral Computed Tomography)
Multispiral computed tomography (MSCT) is a diagnostic imaging technique that uses X–rays to obtain detailed transverse images of the body. In other words, we can say that this is a new generation X-ray, but it significantly surpasses traditional radiography in its ability to depict internal structures in detail.
The MSCT uses a computer and a rotating X-ray machine to create a series of images, which are then processed by a computer, forming detailed transverse images (layers) of the body. In multispiral tomography, the X-ray tube and detectors rotate around the patient while moving along his body, which allows for higher-quality images and shortens the examination time.
MSCT is widely used to assess the condition of bones, lungs, and heart, as well as to detect various pathologies in the abdominal cavity and pelvis. This method is especially useful for rapid diagnosis in cases of injuries, hemorrhages and lung diseases (for example, pneumonia or cancer).
Advantages of MSCT
- Quickness of the study: MSCT can be performed in just a few minutes, which is critically important in emergency situations.
- High capture area: This makes it possible to accurately identify small structures and pathological changes.
Thus, MSCT is a powerful diagnostic tool, especially in situations requiring rapid response and accurate assessment of structural changes in the body.
MRI and MSCT: what is their difference
When choosing a diagnostic method, the question often arises: "What is better: MRI or MSCT?". The answer depends on the specific circumstances, let's try to answer it.
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) and multispiral computed tomography (MSCT) are different diagnostic methods, each of which has its own characteristics and advantages.
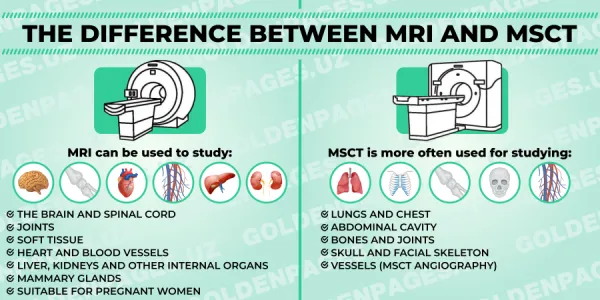
The main differences between MRI and MSCT
- Technology: MRI uses a magnetic field and radio waves to create images, whereas MSCT is based on X-rays.
- Application:
MRI: Especially effective in imaging soft tissues, including the brain, spinal cord, ligaments and joints, due to the high contrast between different types of tissues.
MSCT: It is better suited for studying bones, lungs and abdominal organs by providing detailed images of solid structures.
Other differences
- Procedure time: MSCT is usually a faster and more convenient procedure in emergency situations, taking only a few minutes, while MRI can last from 30 minutes to an hour.
- Patient preparation: MRI requires more thorough preparation, including removal of metal objects and possibly administration of a contrast agent. Preparation for MSCT is usually less complicated, although sometimes it also requires a contrast agent.
- Radiation exposure: MSCT is associated with exposure to ionizing radiation, which may be a risk factor with frequent use, while MRI does not use ionizing radiation and is considered safer for certain groups of patients, including pregnant women.
The choice of diagnostic method depends on the specific medical needs, the patient's condition and the nature of the disease.
MRI is preferable when:
- Diagnosis of soft tissues, neurological diseases (for example, brain tumors, multiple sclerosis, epilepsy).
- The need for multiple scans without the risk of radiation exposure.
MSCT is recommended in cases of:
- Injuries and emergencies for rapid assessment of the condition, especially in fractures, chest and abdominal injuries.
- Diagnosis of diseases of the lungs, chest and blood vessel examination.
Both methods have their advantages and limitations, and the doctor's recommendations play a key role in choosing the appropriate diagnostic method.
What to choose for diagnosis: MSCT or MRI
In conclusion, the choice between MSCT and MRI for diagnosis should be made based on individual medical needs and doctor's recommendations. Each of these methods has its own unique advantages and limitations, and only a qualified medical professional can correctly assess which method is best suited for your particular case. Always consult with your doctor in order to make an informed and safe decision about the diagnostic method that will be best for you. Be healthy!
- Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) in Tashkent
- Multispiral computer tomography in Uzbekistan- services

01.12.2025